Hi,
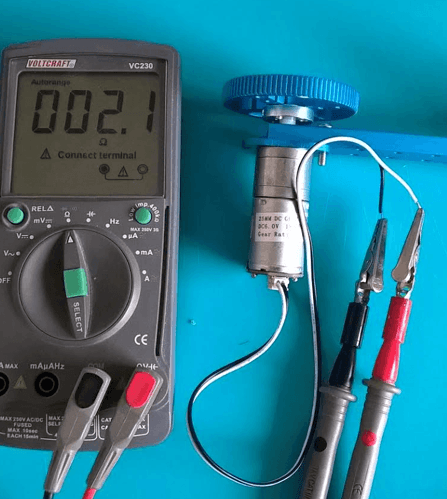
Connect the two motor leads to your multimeter and select the resistance range, see picture.
Note that below 10 Ohm, error of a few Ohms is possible. Make sure you have solid connections and check if the readout of the multimeter is zero when the probes are connected together (without the motor). If not, you can subtract this value from the motor resistance reading.
The resistance measured is an indication of the torque the motor should be able to provide. The supply current is dependent of the turning rate of the motor (and voltage & pwm duty cycle of the supply). And battery voltage will drop when current increases. So for a good comparison, you need supply current, supply voltage and turning rate (at lease some estimate).
Since you seem to have motor that provides insufficient torque to move, it would be interesting to know the current when they are not moving. Use your battery and measure the voltage too (don’t need to measure them simultaniously). If the current is low (with sufficient supply voltage), it’s an electrical problem. If it’s high, you have a mechanical problem. Note that high currents can damage motors, so do not block your motor for this meaurement!